Eutrophication
The main goal of the Working Area Eutrophication is to work towards natural and clean rivers and the reduction of eutrophication in the Baltic Sea.
The problem
Nutrients over-enrichment, mainly nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P), into ground and surface water is the cause of
eutrophication . The main effect of leaching of nutrients is the rapid growth of algae on the surface of the water, a phenomenon called “algae bloom”. When it occurs, the surface layer formed by algae prevents sunlight from getting through it and reaching the bottom, causing decreased water clarity and the death of larger plant species such as seagrass. The loss of plant life represents the destruction of habitats that provided shelter, food and nursery grounds for many marine animals. Moreover, the deposition of organic material – decomposed by bacteria – increases oxygen consumption on the seafloor, which leads to oxygen depletion and creates
dead zones . These now cover 20% of the Baltic Sea bottom. Some algae species are toxic for marine mammals and can also be dangerous for humans.
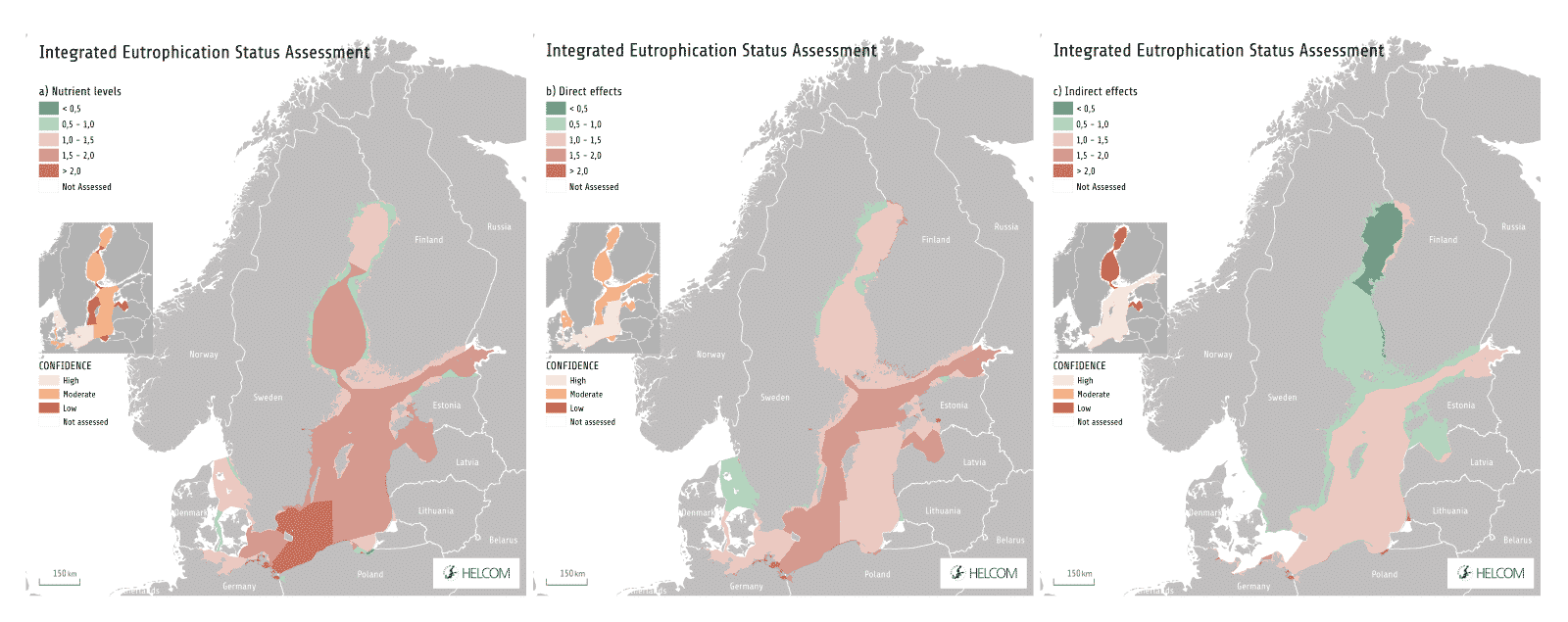
Eutrophication causes reduction of biodiversity, erosion of coasts and impoverishment in fish population. Despite some small improvements, the Baltic Sea is heavily affected by eutrophication (
97% of the surface area ) resulting from excess nutrient loads for many years.
Climate change could also have a negative impact on the Baltic Sea catchment area, exacerbating eutrophication – since water and air temperature rise could create better conditions for the growth of algae blooms.
Where does over-fertilization come from?
Most of the water quality problems in the Baltic Sea originate upstream from the thousands of rivers in the catchment area. Some 25% (25% for Baltic proper, 20% for Baltic Sea) of the nutrient load in the Baltic Sea comes from waste water and upstream sources of pollution – not only from farms, but also from households and ports.
According to CCB´s estimates potential losses from 22 million tons of fertilizers handled in the Baltic ports annually may account up to several thousand tons of directly bioavailable nitrogen and phosphorus.
- Landscape transformation
- Loss of biodiversity
- Greenhouse gas emissions
- Livestock production waste and overfertilization
- Deterioration of the quality of life of local residents
- Legislation and legal problems
- Climate change
Currently, 60% of our European rivers and lakes are in poor condition. A freshly given analysis CCB participated in, points out that, only Finland, amongst EU countries, is on a good track to reach Water Framework Directive (WFD) goals and legally binding EU target to return Europe’s dirty freshwaters to health by 2027. There is still a lot to improve, also for our health & safety.
The goal
The aim is to achieve a Good Environmental/Ecological Status (GES) of rivers draining to the Baltic Sea as having
an immense importance for reducing pollution and nutrients inputs, as well as for conservation of biodiversity.
We want to ensure a good supply of clean drinking water to all inhabitants in the Baltic Sea Region and to develop systems for an ecologically sustainable production and handling of waste water.
Addressing nutrient losses in agriculture, poor handling of fertilizers in shipping, manure handling related to industrial animal farming and general overfertilisation – these aspects contribute to reaching the goals of the EU Circular Economy Action Plan through closing the nutrient loops.
How is CCB working with this issue?
MATERIALS & MEDIA
WHAT CAN WE DO?
What can countries do together?
- Joint action should focus on the application of sustainable, ecologically-oriented solutions for wastewater treatment, with a high degree of nutrient recycling, clear and measurable targets in water management;
- Work together to promote ecologically sustainable agricultural practices within the framework of the recommendations under HELCOM;
- Reform the Common Agriculture Policy (CAP) to promote sustainable agriculture via coupling EU agricultural subsidies with requirements to take measures to substantially reduce the nutrient run-off to water from agricultural production;
- Improvements and efficiency in water management, working towards river connectivity and river restoration (including dam removal).
What can each country do?
- Develop national programmes for the implementation of the HELCOM agreement on wastewater management and water savings as the saving of water instead of wasting it is the most effective way to avoid water pollution problems;
- Promote the use of sustainable wastewater technologies, including nutrient recycling approaches that are particularly suitable for the treatment of wastewater from small to medium sized sources;
- Introduce environmental conditionality on all agricultural subsidies, such as requirements for nutrient-balanced fertilization;
- Promote the use of less intensive, organic farming practices;
Reduce emissions from land and maritime traffic; - Ban open cage fish aquaculture;
- Raise consumer awareness on limiting meat consumption;
- Improvements and efficiency in water management with clear measures and targets, taking climate change and nature based solutions into consideration, working towards river connectivity and river restoration (including dam removal).
What can you do?
- Be aware in your everyday life of the need to save water and make sure you save as much water as possible;
- If it is feasible then you can introduce new toilet system in your home or at your workplace that includes direct nutrient recycling to farmland;
- You can also try to convince your municipality of the importance of eco-technological solutions, including the use of natural systems e.g. constructed wetlands;
- Support sustainable agriculture by actively asking for and buying products which are certified to have been produced with sustainable methods;
- Avoid over fertilizing your own garden and using pesticides;
- Engage in your national or/and local groups and organizations working towards good ecological state of rivers.
Get in contact with the
CCB Working Area Leader on Eutrophication
If you have questions or want to collaborate
send an e-mail to:
secretariat [at] ccb.se
We continue to act, do you want to know more?
Click the button below to discover our other Working Areas.